Dialogue is an important code that has the purpose of imparting information to the audience and establishing characters and relationships. The mode of address of the speaker and their specific lexis (language) can anchor the text in a particular genre.
Sound effects add to the realism of the product and are also often a key indicator of genre (many genres enhance these for effect).
Narration is an example of non-diegetic sound that serves to give information to the audience. Often accompanies film-trailers to fill-in missing pieces of the plot for the audience.
The choice of this usually conveys narrative information and suggests genre. For example, there is an expectation that, at tense moment in a TV crime drama, appropriate non-diegetic music will be heard. Audiences will suspend disbelief as it adds to the atmosphere.
Close-ups are used to create emotion and tension. Often used to make the audience feel involved with a character.
Extreme close-up, for example a hand on a door handle, where information is withheld from the audience, create suspense or draw attention to something important that will be used later in the narrative.
Medium close-up also called 'newsreader shots'. The head and shoulders shot is how the audience would expect a news anchor to be within the frame.
Long shots. Used when more information is required. Here the audience may be shown the characters and part of their surroundings to enhance their understanding of the scene.
Establishing shots are rapid ways of advancing the narrative by showing the audience where the action is about to take place. Audiences may then have expectation about what will happen next.
Tracking shot is when the camera follows the character or action. The effect is to make the audience feel involved in the action.
Zoom is when (typically) the camera moves from long shot towards the subject. They should be smooth and unnoticeable (unless that is the desired effect), allowing the audience to move to a close-up and be involved in the emotion of the character.
Costume helps the audience identify/understand the role of a character and creates audience expectations of their behaviour.
Panning shot is when the camera moves across the scene, imparting knowledge to the audience. Often used to show location. In a whip technique the camera moves at high speed causing a blurring effect suggesting pace and action.
Tilt is when the camera moves vertically from top to bottom, or vice-versa. It can be used to imply mystery when introducing a character, slowly lifting the camera from feet to face.
Expression is a way in which messages between characters can be communicated non-verbally. Allows emotion to be clearly represented, used in combination with a close-up.
Gesture is another non-verbal communicator used to express emotion visually. For example a shrug, a wave or something more aggressive or offensive.
Iconography: objects, settings and backgrounds within media products that contain meaning.
Colour: the way in which a product is constructed and presented conveys meaning. For example, the use of black and white may suggest sophistication, soft focus may carry connotation of romance.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Cast & Crew
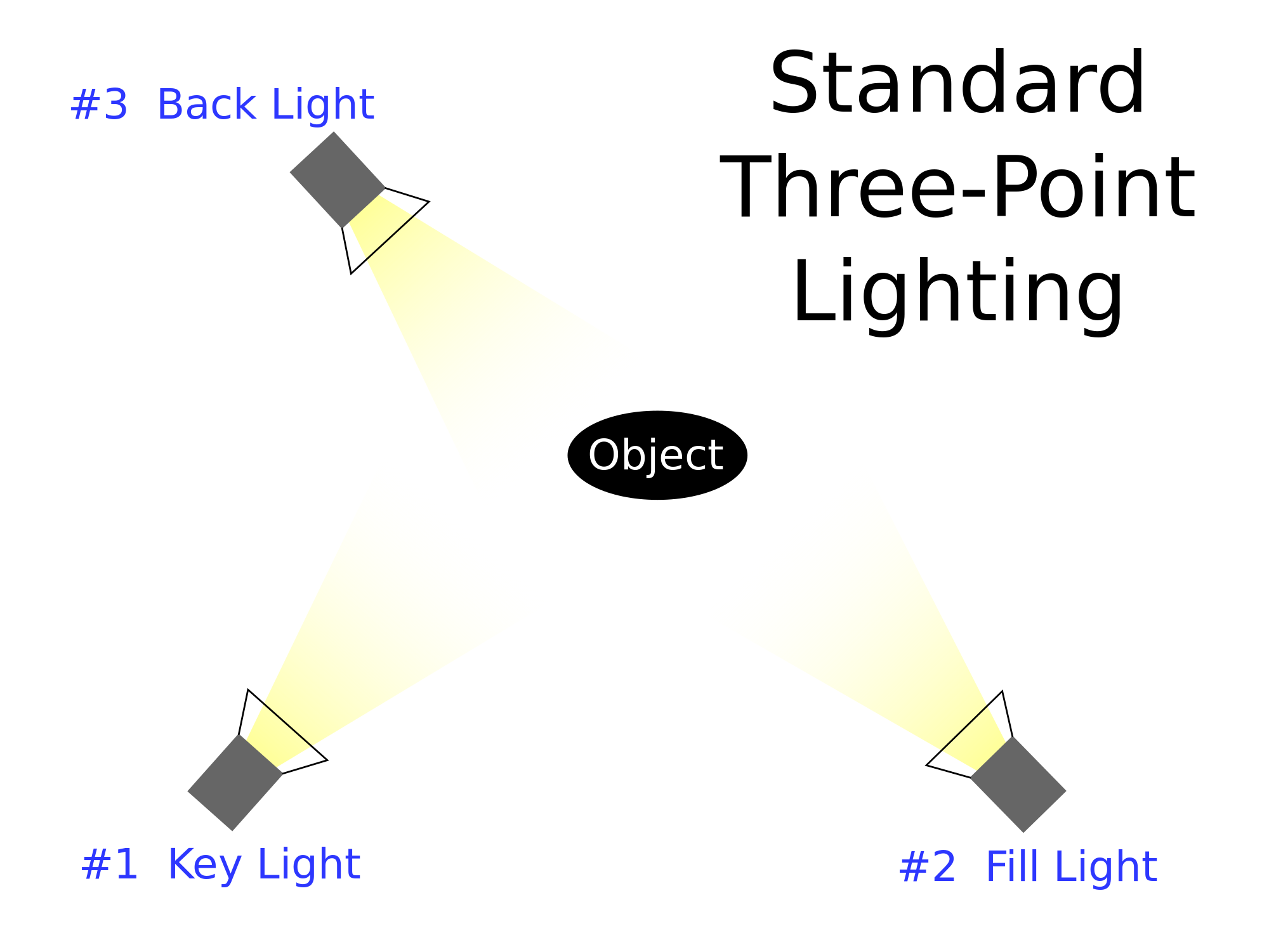
When taking the Cast and Crew photos, we used 3-point lighting. This meant that a key light was facing the subject, a fill light was ...
-
Dialogue is an important code that has the purpose of imparting information to the audience and establishing characters and relationships. T...
-
MANAGEMENT Production Manager Managing the production budget. Making sure the production runs smoothly for the Producer and Line Pro...
-
Proposal Story Outline Script Budget Storyboards Locations Location Permission Crew List Talent List Risk Assessments Equipment ...
No comments:
Post a Comment