MANAGEMENT
Production Manager
- Managing the production budget.
- Making sure the production runs smoothly for the Producer and Line Producer.
- Scheduling shoots and negotiating hire of crews and equipment.
Location Manager
- Finding ideal locations for a film shoot.
- Negotiating fees, terms and permissions.
- Managing the location during the shoot.
Construction Manager
- Supervising the construction of sets and stages for film productions.
- Leading a team of craftsmen, including Carpenters, Painters, Riggers and Plasterers.
- Ordering tools and materials and staying within budget.
Producer
- Turning story ideas into profitable films.
- Putting together a creative and talented cast and crew.
- Being responsible for all aspects of a film's production.
Director
- Being the driving creative force in a film's production - visualising and defining the style and structure of the film, then bringing it to life.
- Carrying out duties such as casting, script editing, shot composition, shot selection and editing.
- Acting as the crucial link between the production, technical and creative teams.
CREATIVE
Actor
- Interpreting others' words in order to bring a script to life, and to put flesh and blood on characters.
Make-up and Hair Artist
- Creating make-ups and hairstyles to meet production requirements.
- Overseeing make-up and hair continuity during filming.
- Working to the Make-up and Hair Designer's brief.
Costume Designer
- Being in charge of designing, creating, acquiring and hiring all costumes for Actors and extras.
- Managing a team of skilled personnel.
- Supervising practical issues, such as departmental budgets and schedules, the organisation of running wardrobes, and costume continuity.
Sound Designer
- Creating sound effects for giant explosions or car crashes.
- Creating more subtle sounds to enhance mood and feeling.
- Managing the sound post production process.
Set Decorator
- Analysing the script and listing all items needed for the film set.
- Finding, hiring or commissioning props.
- Keeping detailed records before and during shooting and returning all props when they're no longer needed.
TECHNICAL
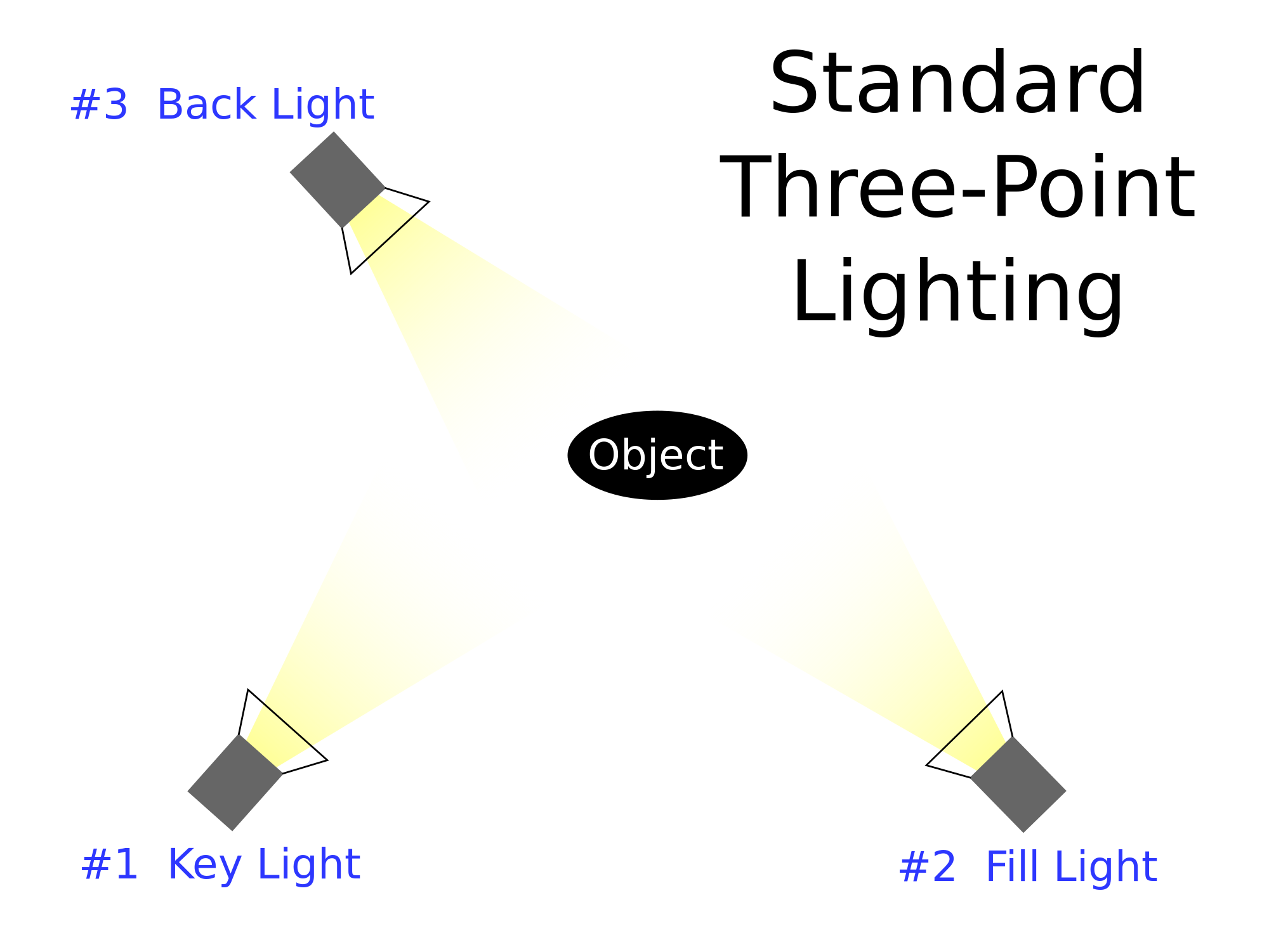
Lighting Technician
- Looking after lighting equipment on a film set, or on location.
- Helping with the power supply.
- Helping to set up lighting equipment.
Gaffer
- Running all the electrical work on a production.
- Leading a team of lighting technicians.
- Working closely with the Director of Photography.
Crane Operator
- Setting up and operating all cranes, which carry cameras and crew.
- Working closely with Grips and Camera Operators.
- Making sure safety procedures are closely followed.
Camera Operator
- Preparing and operating the camera and all its equipment.
- Working with the Director and Director of Photography to achieve the visual style of the film.
- Managing other camera department staff and communicating with Actors.
Console Operator
- Operating fixed lights on a film set.
- Mixing lighting effects during filming.
- Setting up and maintaining lighting consoles.